A task management system for multi-site food service operations. Plan, verify & document CCPs with drag&drop-efficiency.
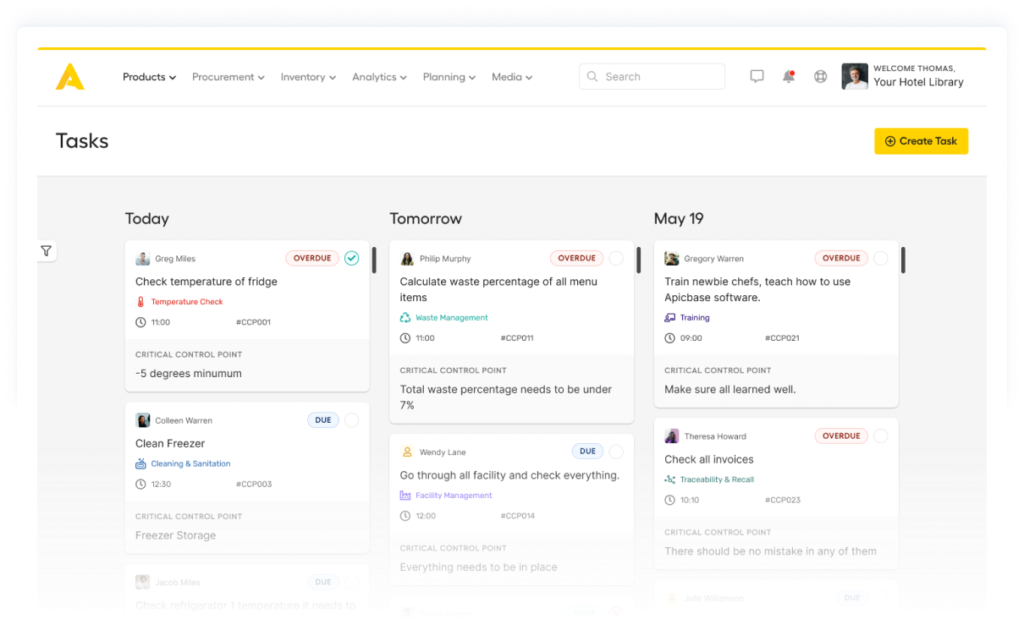


Roll-out food safety plans group-wide.
Monitor, verify and log all tasks in one place.
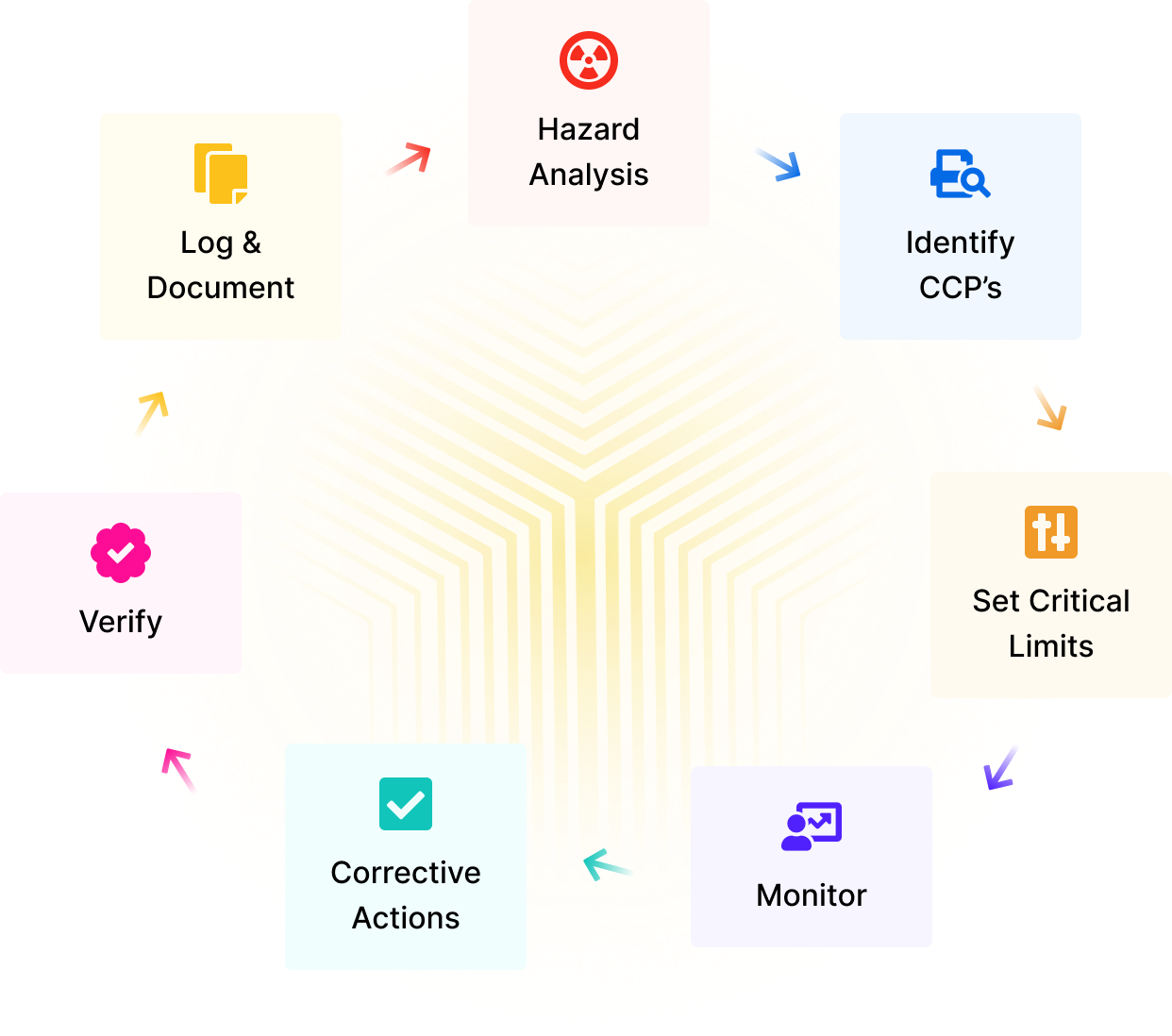
Manage food safety processes and documentation in one workflow.
Fill out the core elements of your HACCP plan in the system, including minimum and maximum levels. The CCPs can be created group-wide, per outlet or workstation.
Know who to talk to when execution doesn't meet the guidelines. People are accountable for their job.
Generate thorough haccp reports at the touch of a button. Should there be any anomalies, staff can take immediate corrective actions and register them in the system.
Your staff has access to detailed task descriptions ensuring flawless execution
The easy calendar view allows you to see if things are going according to plan. Monitor group-wide performance in a single dashboard.
Your food safety records are ready for audits. They are stored in the cloud and searchable by location, date, task and staff member.
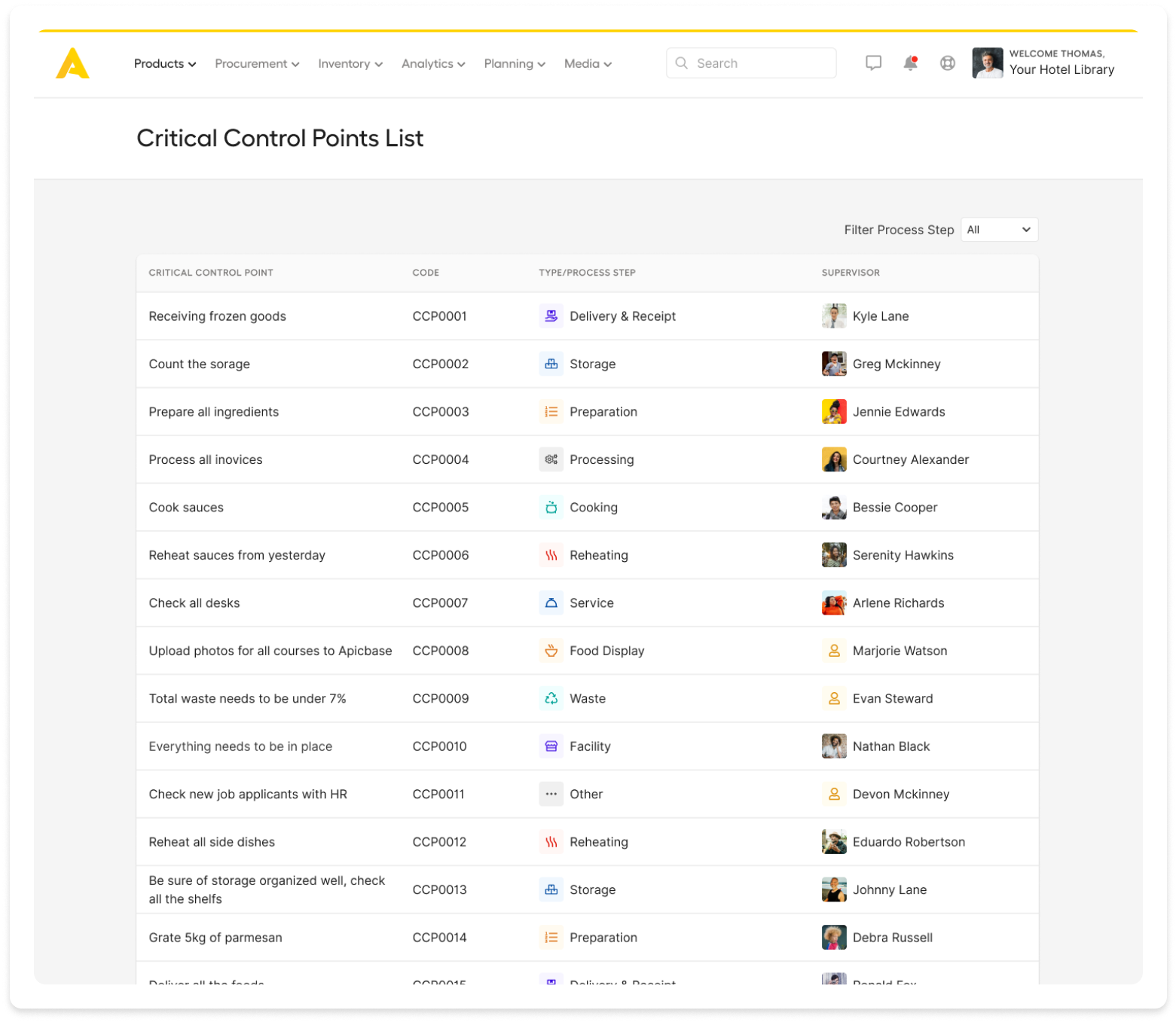
Avoid the administrative nightmare and get an easy-to-use interface for planning, monitoring & documenting HACCP tasks.


Apicbase has been an absolute godsend. Our local EHO officer came round to check on compliance. I showed him the system and explained how effective it is.
Chef
Apicbase NV – 2025. All Rights reserved
Apicbase is the most complete F&B management platform for multi-unit restaurants, hotels, ghost kitchens.