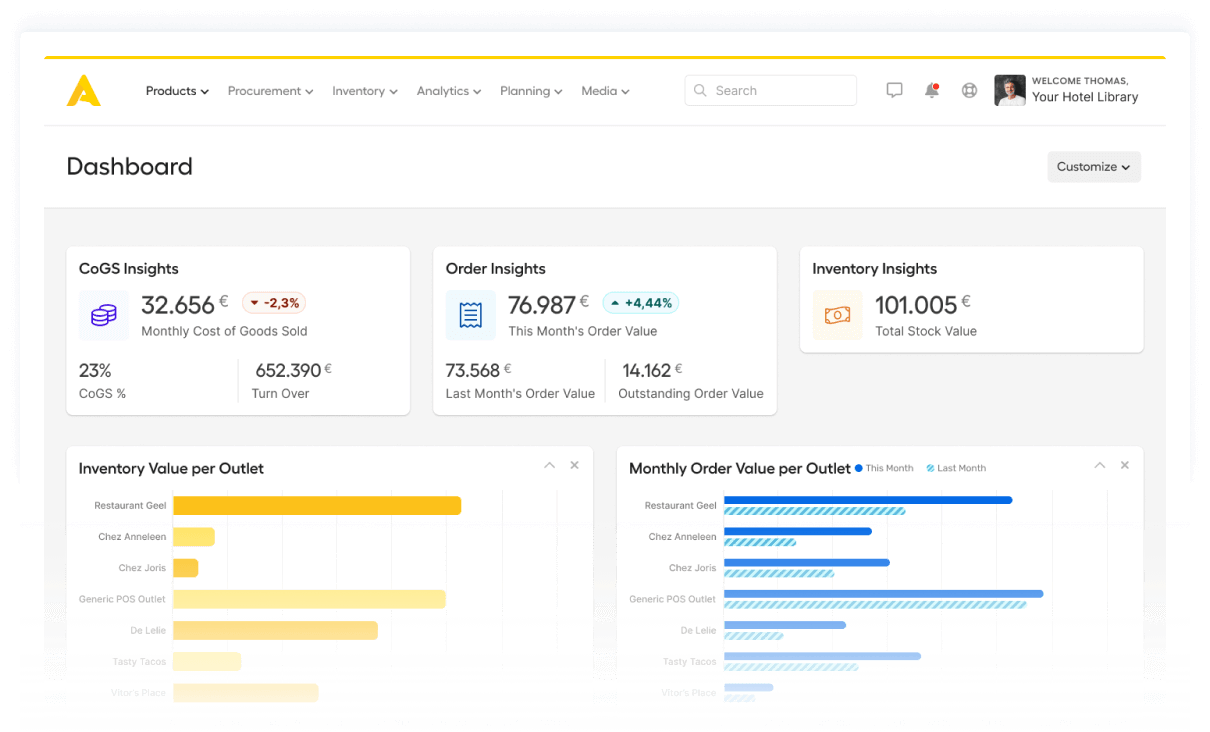
The data you need to engineer profitable menus with best-selling items is at your fingertips. Your COGS and sales per item are combined in a single matrix to help you tune menus to perfection.

Arm your menu engineers with real-time sales and cost insights. Your creativity is backed by objective data. That’s a force to be reckoned with.
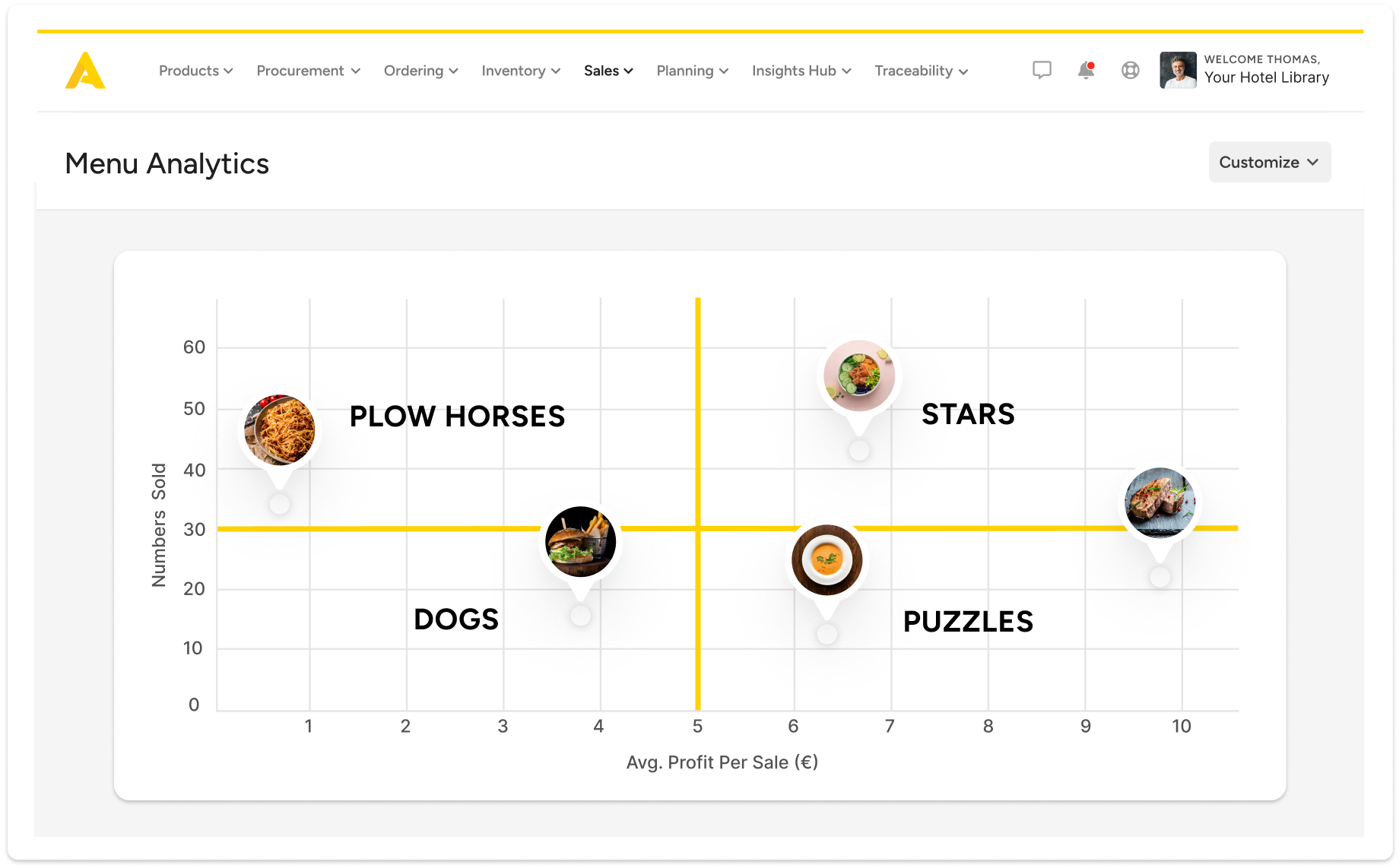
Data-driven menu engineering. Everything you need to know sits in a single graph. Identify dishes that are both popular AND profitable - in a flash.
Go granular. Get the numbers on whole categories, menus or specific items. And let Apicbase sort them out.
Real-time sales and cost data guides your choices. It helps you bulletproof the menus and detect underperforming products.
Underperforming menu-items have nowhere to hide.
Understand sales numbers, revenue, prime costs, profit & margins.
Get the facts on every menu item. Know when to revise, promote or retire a dish.
Find your cash cows and menu stars in a flash. Get a full breakdown of a menu in a single matrix.
Document your sales analysis anyway you want. Heck, you can even highlight those big profits bright yellow on a printed copy.
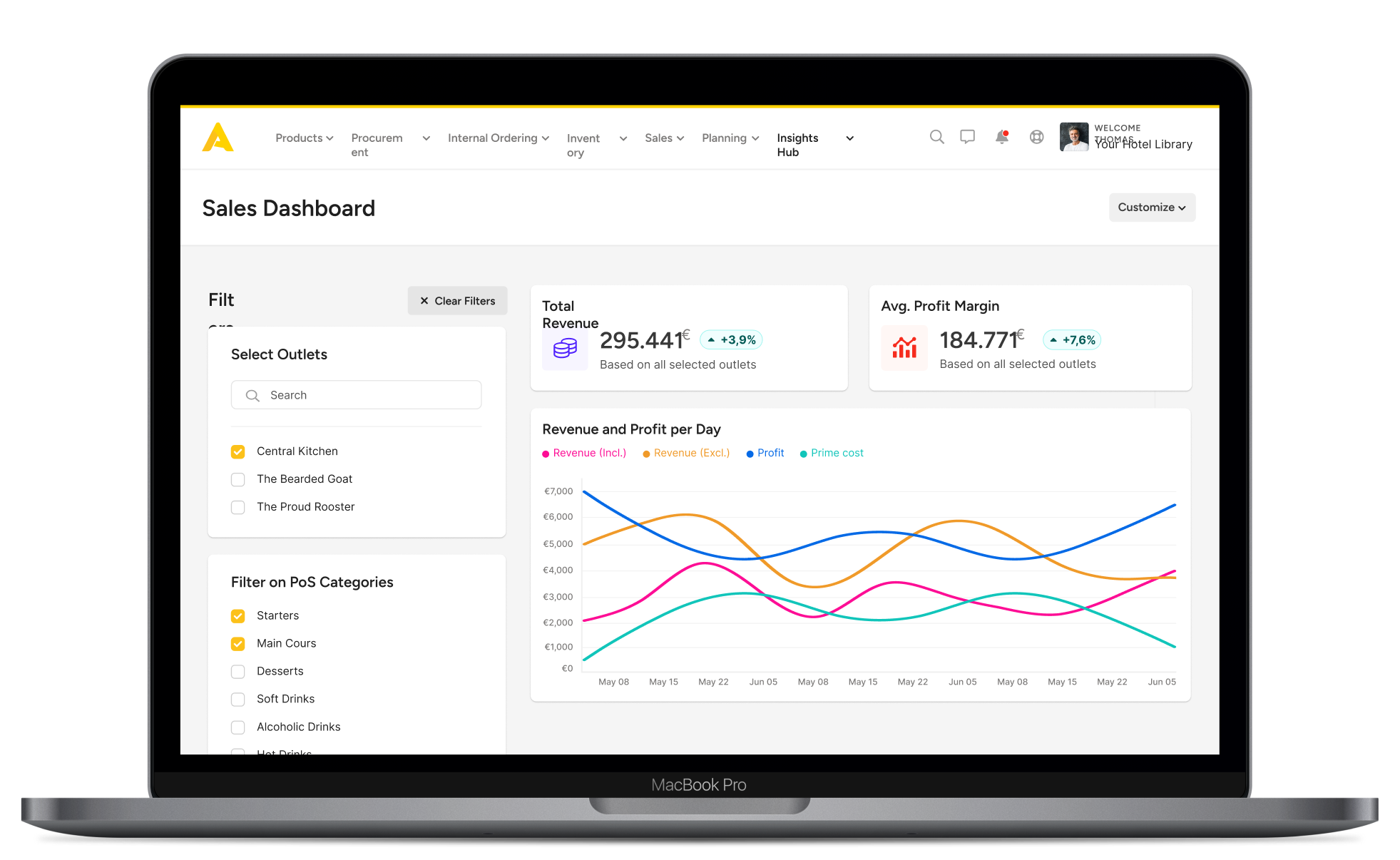
Focus on strategic menu-engineering that consistently boosts sales across every store location.


Apicbase helps us decide which menus to kill, how to optimise procedures and how to better deal with food cost. Our business is built on reliable data.
CEO
Bright Kitchen
Apicbase NV – 2025. All Rights reserved
Apicbase is the most complete F&B management platform for multi-unit restaurants, hotels, ghost kitchens.