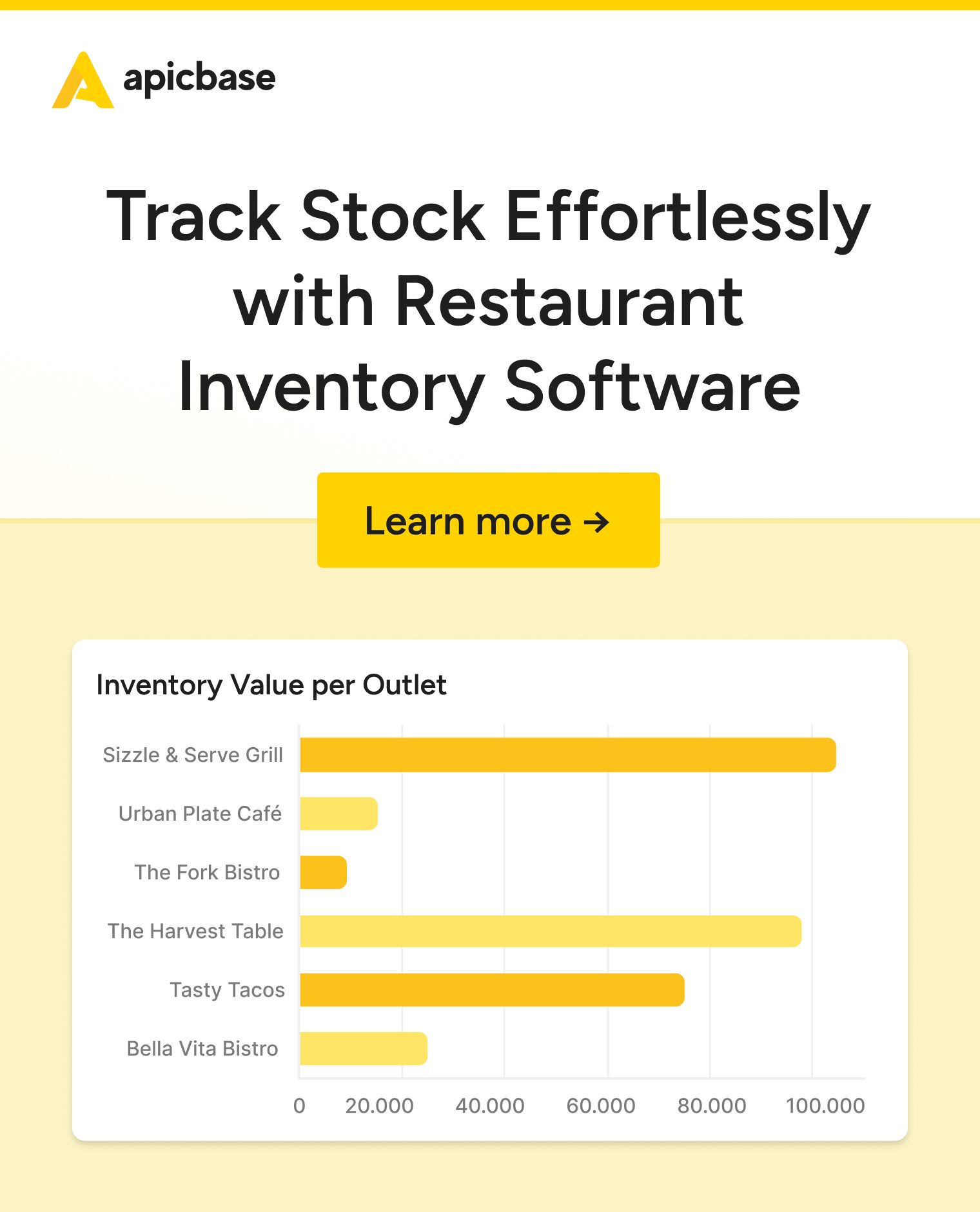
Struggling with restaurant inventory management? You’re not alone—58% of operators say rising inventory costs are their biggest financial challenge.
The good news: you can take back control. While ingredient prices may fluctuate, improving your inventory processes can add 2–10% to your bottom line every week.
This guide will show you how to refine your inventory system and protect your profit margins.
What is Restaurant Inventory Management?
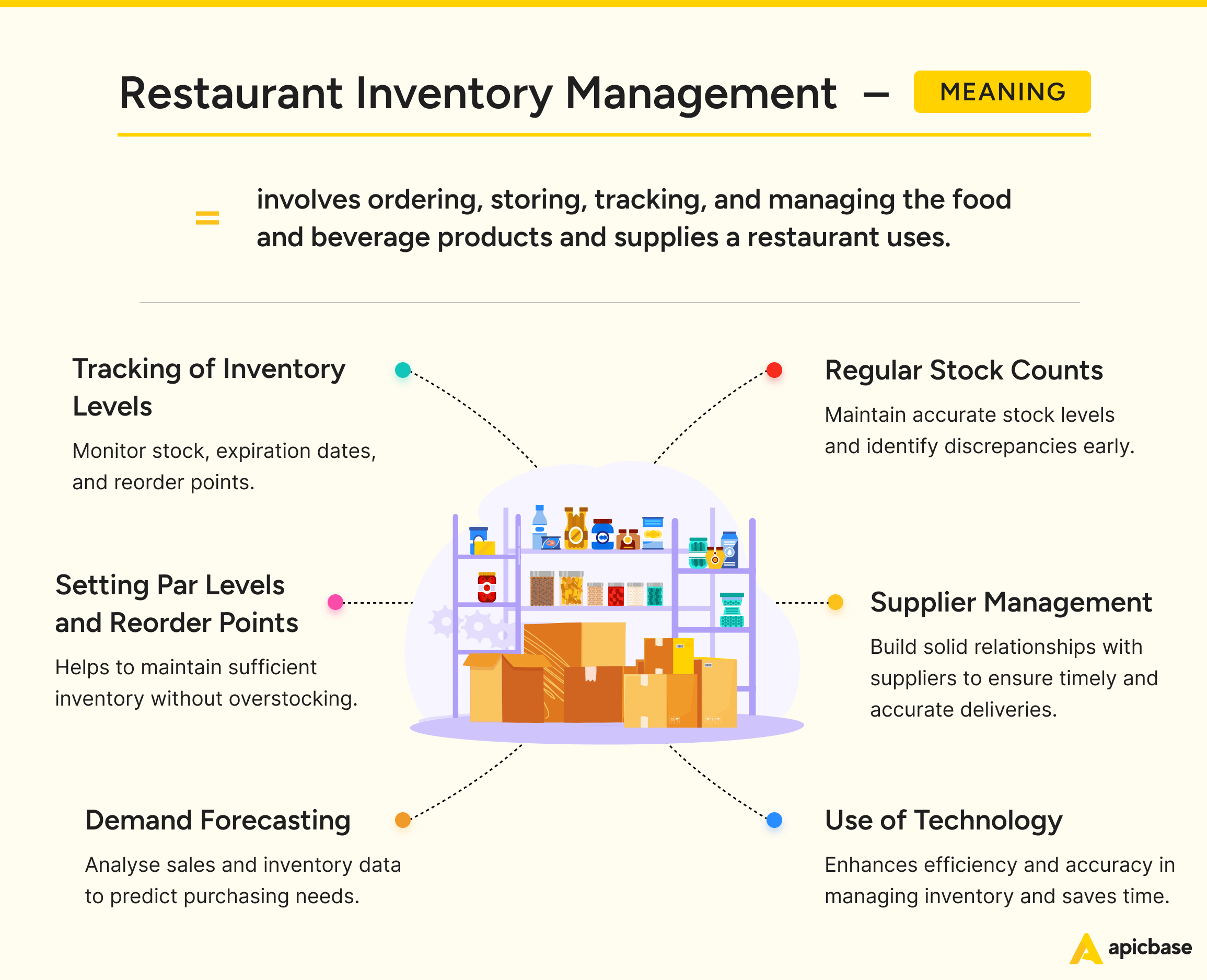
Restaurant inventory management is an essential process for food service businesses. It involves tracking and organising the stock levels of ingredients and supplies needed for food preparation and service.
This systematic approach includes monitoring items from when they arrive until they are used, sold, or thrown away.
Smaller operations often use spreadsheets for inventory tasks (Grab our free inventory sheet for Excel and Google Docs).
Larger, more complex businesses turn to restaurant inventory management software for its automation, accuracy, and detailed reporting.
The core components of restaurant inventory management include:
- Tracking and Monitoring: Inventory management covers everything from ingredients and beverages to cooking equipment and non-food items like linens and uniforms. It starts the moment items are delivered and continues until they’re used or disposed of, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
- Stock Level Optimisation: The goal is to maintain just the right amount of stock to meet customer demand without overstocking. Menu engineering complements this by identifying your most profitable dishes, helping you align your stock with what sells best. Overstocking ties up capital and increases waste, especially with perishable items, making this a constant challenge in food service.
- Actual vs Theoretical Stock Comparison: Theoretical stock is based on purchase orders, while actual stock is determined through physical counts. Ideally, these numbers should align. Any discrepancy signals inventory losses—and lost profits.
- Demand Forecasting: By anticipating demand fluctuations through seasonality, events, and historical data, restaurants can make smarter purchasing decisions, reduce waste, and improve efficiency.
Track your inventory in real-time with precision
With restaurant inventory software, you take back control.
Benefits of Restaurant Inventory Management
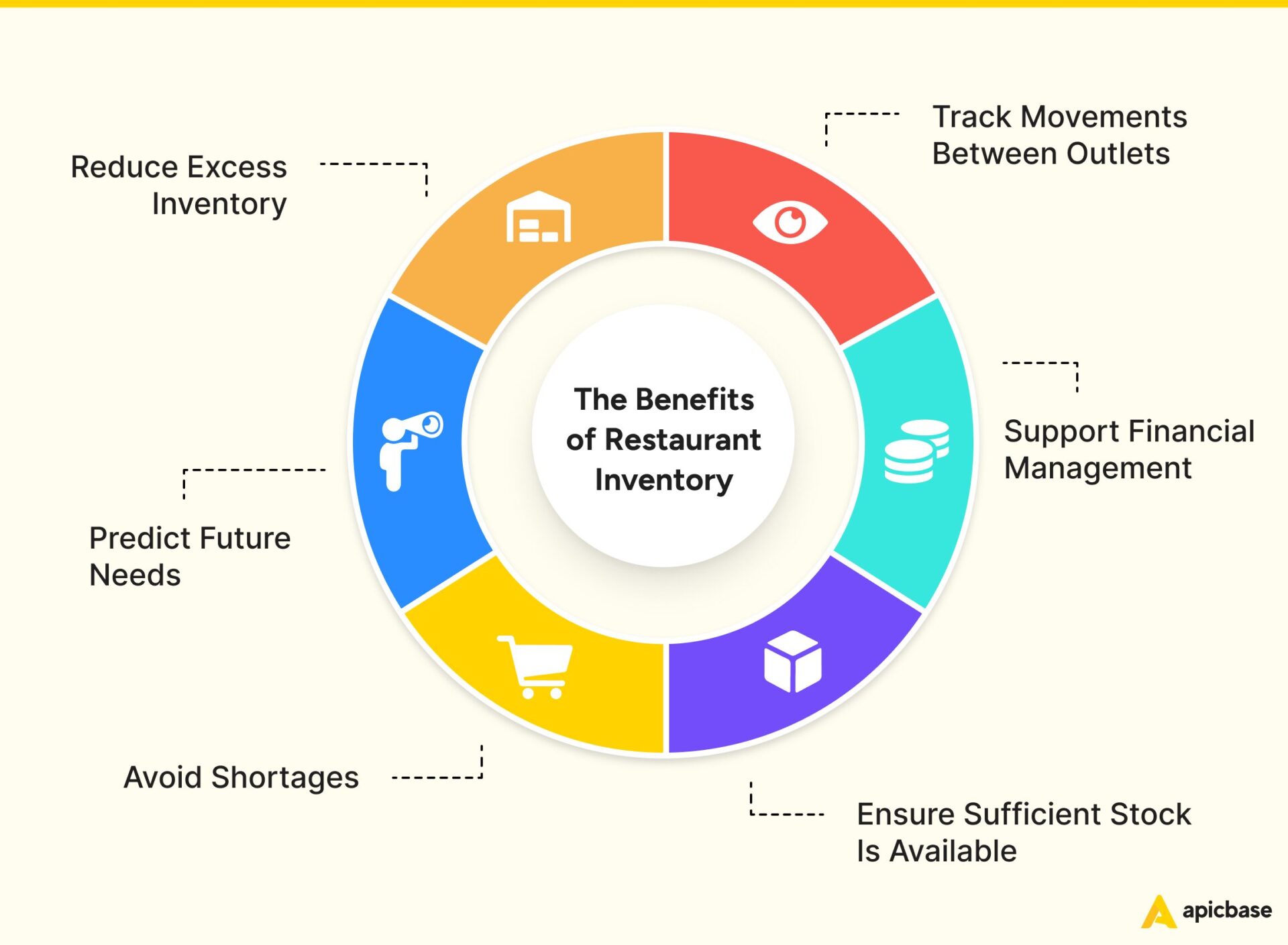
Effective food inventory management does six key things:
- Reduces excess stock.
- Predicts future needs.
- Prevents shortages.
- Tracks stock levels.
- Calculates food costs.
- Monitors supply movements between locations.
This, in turn, allows you to:
1. Get a Clear View of Your Business’s Health
Food cost variance—a measure of the gap between theoretical and actual costs—reveals how well your restaurant manages inventory. Large variances signal problems like waste, theft, or poor purchasing decisions, all of which eat into profits. Tight inventory processes keep these leaks in check, helping you maintain healthy margins.
2. Lower Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Accurate inventory tracking reduces unnecessary spending and ensures optimal use of ingredients. By lowering COGS, you increase your gross profit margin.
The formula to calculate COGS is:

COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchased Inventory − Ending Inventory
As you can see, accurate inventory tracking at the start and end of each period is critical.
Here’s a clear example of how reducing food costs can boost your profit.
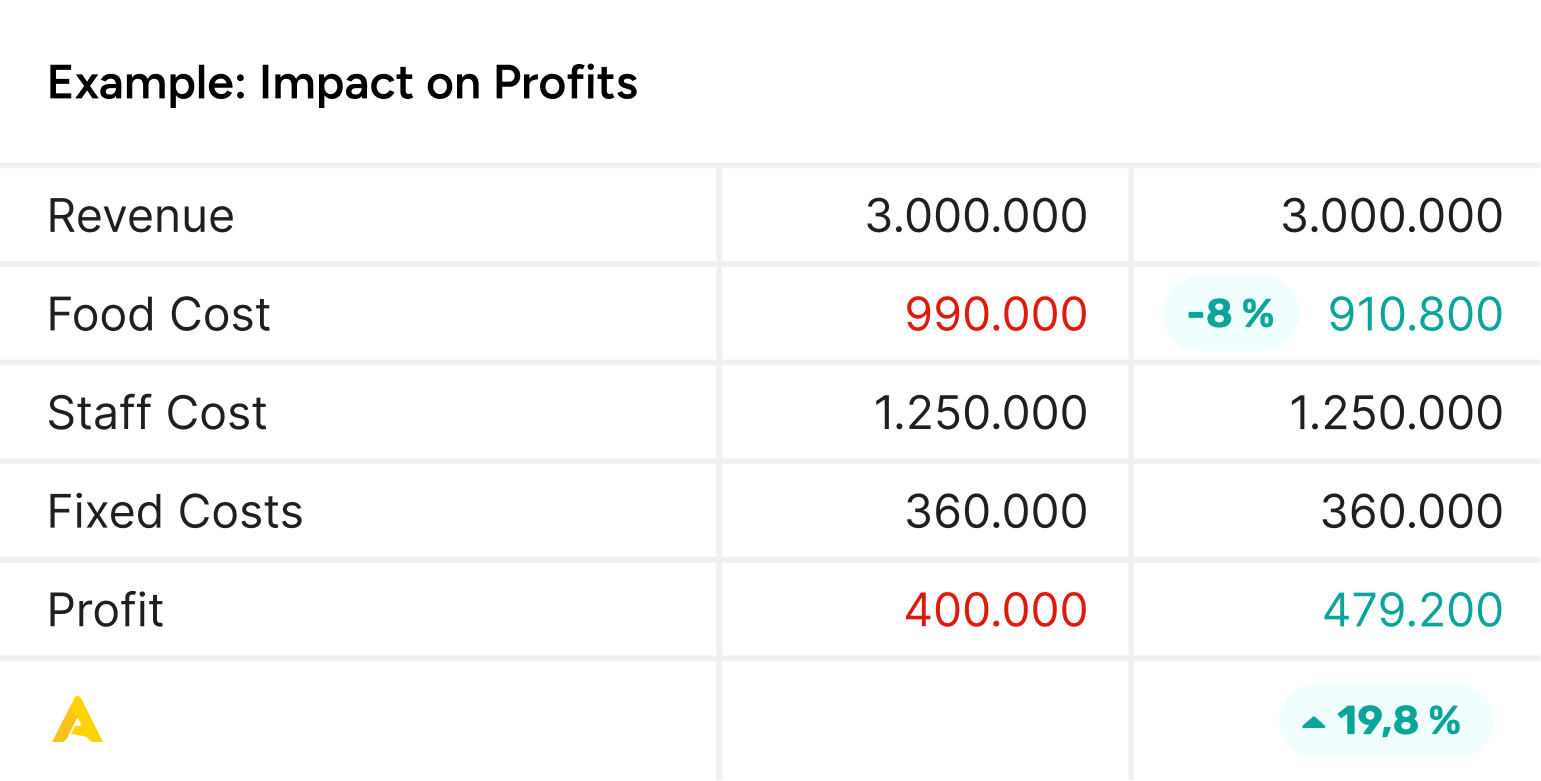
Initial situation:
- Revenue: 3.000.000
- Initial food Cost: 990.000 (33% of Revenue)
- Staff cost: 1.250.000
- Fixed costs: 360.000
Initial profit calculation:
- Initial Profit: Revenue – (Food Cost + Staff Cost + Fixed Costs)
- Initial Profit: 3.000.000 – (990.000 + 1.250.000 + 360.000) = 400.000
After improved inventory control:
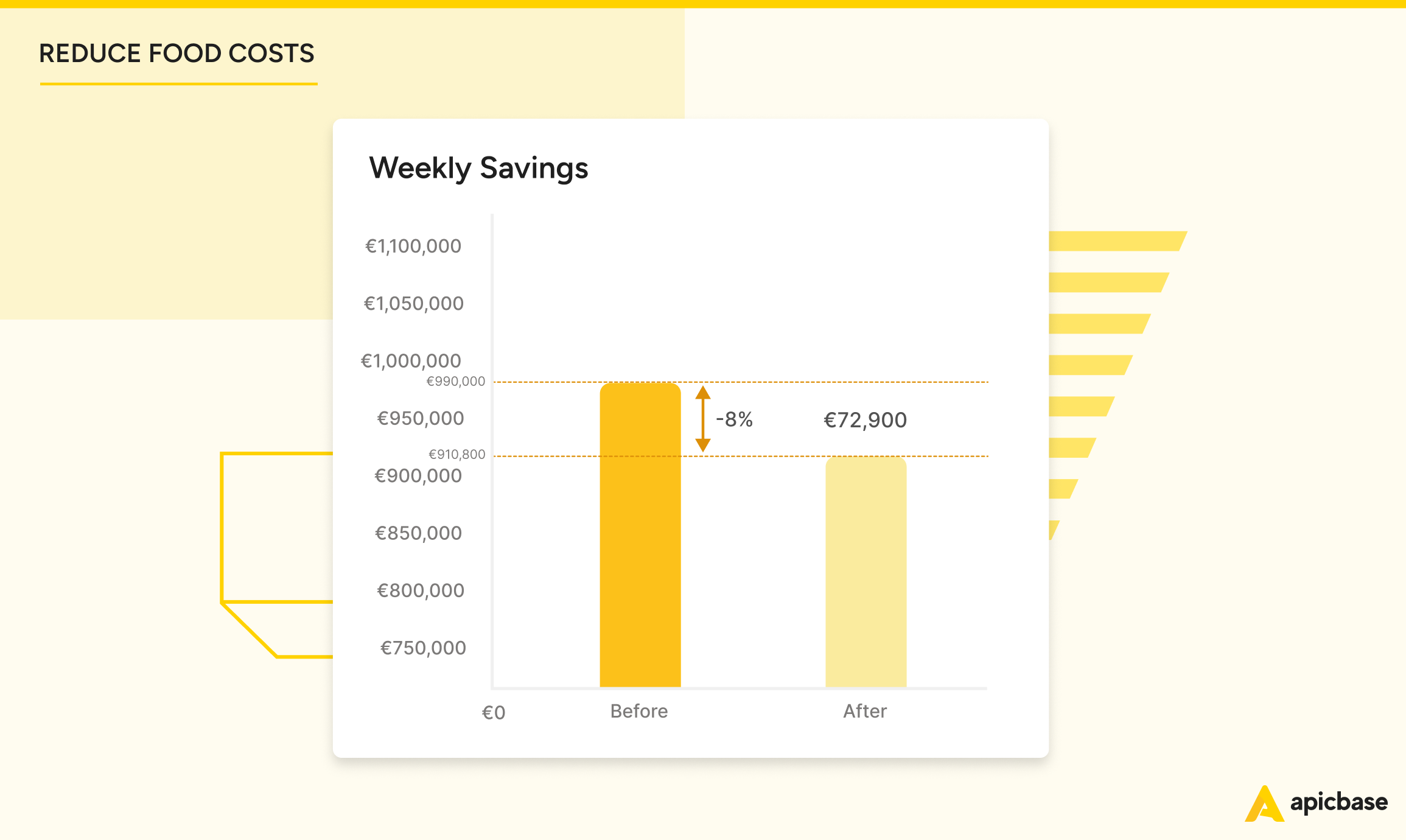
- Reduction in Food Cost: 8% of the initial Food Cost
- Reduction Amount: 990.000 * 0,08 = 79.200
- New Food Cost: 990.000 – 79.200 = 910.800
New profit calculation:
- New Profit: Revenue – (New Food Cost + Staff Cost + Fixed Costs)
- New Profit: 3.000.000 – (910.800 + 1.250.000 + 360.000) = 479.200
Impact on profit:
- Increase in Profit: New Profit – Initial Profit
- Increase in Profit: 479.200 – 400.000 = 79.200
- Percentage Increase in Profit: (Increase in Profit / Initial Profit)*100
- Percentage Increase in Profit: (79.200 / 400.000)*100 = 19,8%
Proper inventory management and analytics lead to significant cost savings.
In this example, an 8% reduction in food costs saved €79,200, boosting the restaurant’s profit by 19.8%. Sustaining these savings over a year would add €950,400 directly to the bottom line.
3. Avoid Overstocking and Shortages
Too much inventory ties up cash, hurting cash flow, and often leads to waste. Having too little risks stockouts and disappointed customers. Overstocking ties up cash in unused inventory, limiting your ability to invest in other areas. Managing inventory efficiently helps improve cash flow by ensuring your money isn’t sitting on shelves. Smart restaurant inventory management systems help you find the perfect balance, ensuring you order just enough to keep customers happy and costs low.
4. Reduce Food Waste
You can prevent spoilage and excess with clear stock tracking and demand forecasting. The variance reports show you where the inefficiencies in your workflows are or where theft occurs. A high inventory rotation ensures nothing goes to waste. Also, Moving supplies between locations also helps make the most of your resources.
5. Make Smarter Decisions
Accurate data enables strategic choices, from optimising menus with menu engineering to negotiating better supplier deals. Managers can fine-tune purchasing, chefs can adjust pricing, and procurement teams can secure cost-effective terms—leading to greater efficiency and profitability.
6. Improve Profit Margins
By optimising purchases, reducing waste, and improving efficiency, inventory management directly enhances your profit margins. It ensures your restaurant’s most valuable asset—its food—is used effectively, driving sustainable financial success.
14 Cost-Cutting Restaurant Inventory Management Best Practices
We work closely with supply chain, F&B, inventory, and operations managers. Their insights helped us develop tips and best practices for restaurant inventory management.
Here they are:
- Use integrated inventory management software: Start with robust software like Apicbase that connects your POS, inventory, procurement, and supplier databases. Real-time tracking and detailed analytics simplify stock management, automate reordering, and reduce errors.
- Combine periodic and perpetual systems: Use regular physical counts alongside continuous tracking through software. This dual approach keeps records accurate and catches issues like theft or waste early.
- Standardise processes across locations: Implement consistent practices for stock rotation (e.g., FIFO), receiving, storing, and reporting inventory. Standardisation minimises waste, ensures data reliability, and enables benchmarking across sites.
- Standardise recipes and portions: Create consistent recipes and portion sizes to control costs and improve forecasting. Tools like Apicbase automate food cost, nutritional, and allergen calculations, ensuring accuracy across all locations.
- Reduce menu complexity and cross-use ingredients: Simplify your menu and use ingredients across multiple dishes. This streamlines inventory management, reduces waste, and increases the likelihood of bulk discounts.
- Train staff regularly: Teach staff how to handle inventory, use software, and prevent losses. Well-trained employees reduce mistakes, protect goods, and ensure accurate record-keeping.
- Conduct regular audits: Regular or surprise audits reveal inefficiencies, theft, waste, or supplier fraud. With software like Apicbase, you can easily compare actual stock counts to theoretical levels, quickly flagging discrepancies that need action.
- Optimise minimum and PAR levels: Set ideal stock levels using historical data and lead times. This prevents overstocking, reduces waste, and ensures critical items are always available.
- Optimise order frequency: Find the right balance between frequent, smaller orders and bulk purchasing. Tailoring your approach to each location ensures cost efficiency and avoids overstocking.
- Forecast demand with data: Use sales data, trends, and market analysis to predict demand accurately. Apicbase’s procurement module helps you avoid overstocking and reduce waste by automating demand forecasts.
- Integrate with suppliers: Connect your inventory system directly with suppliers for seamless order management. Apicbase provides real-time pricing, availability, and lead times, streamlining the procurement process.
- Evaluate supplier performance: Regularly assess suppliers on delivery times, accuracy, quality, and feedback. Dashboards in Apicbase highlight discrepancies, enabling informed negotiations or supplier changes when needed.
- Focus on scalability: Choose systems that grow with your restaurant business. Scalable solutions accommodate new locations, central kitchens, and complex operations without disruption.
- Keep Improving: Inventory management is never done. Keep analysing inventory reports and KPIs. Update practices based on market changes, feedback, and data insights to optimise efficiency and accuracy.
5 Food Inventory Issues Only Data Analysis Will Uncover
If you are a restaurant data analyst, you’ll love this next section. While everybody is talking about ‘data’, you know what matters is insights.
Data are just rows of numbers, which is not very helpful when you have an actual restaurant to run. But combined in the right way, the numbers tell a story. They surface why your inventory management process isn’t working.
We have discussed food cost variance, inventory turnover rate and days’ sales in inventory. Here is what these metrics uncover:
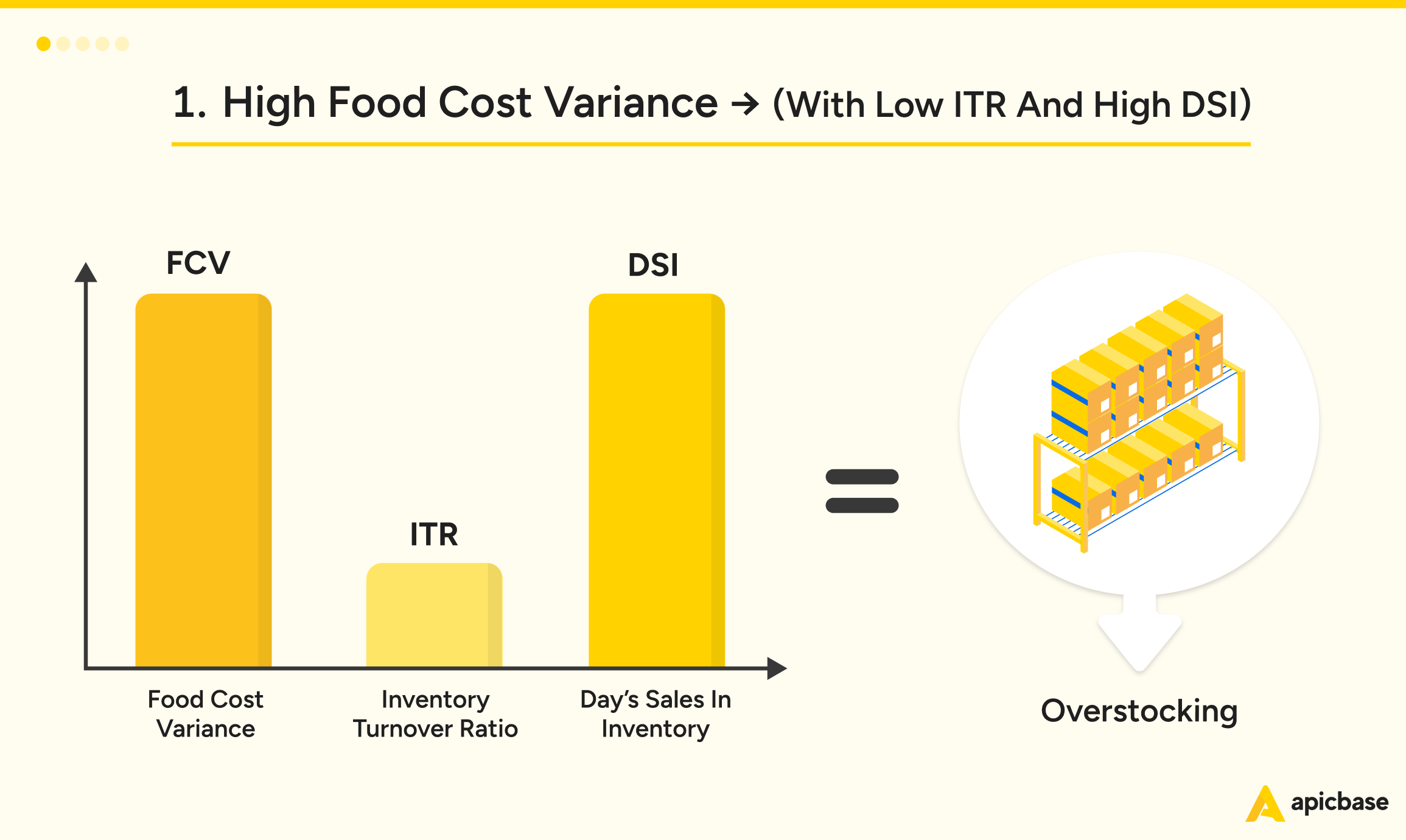
High food cost variance, combined with low inventory turnover (ITR) and high days sales in inventory (DSI), is a clear sign of overstocking. Too much of what you purchase is sitting on shelves, wasting away, while your team sticks to outdated order lists.
To fix this:
- Audit Your Stock: Identify surplus items that are over par levels.
- Adjust Orders: Stop ordering those items until quantities are back under control.
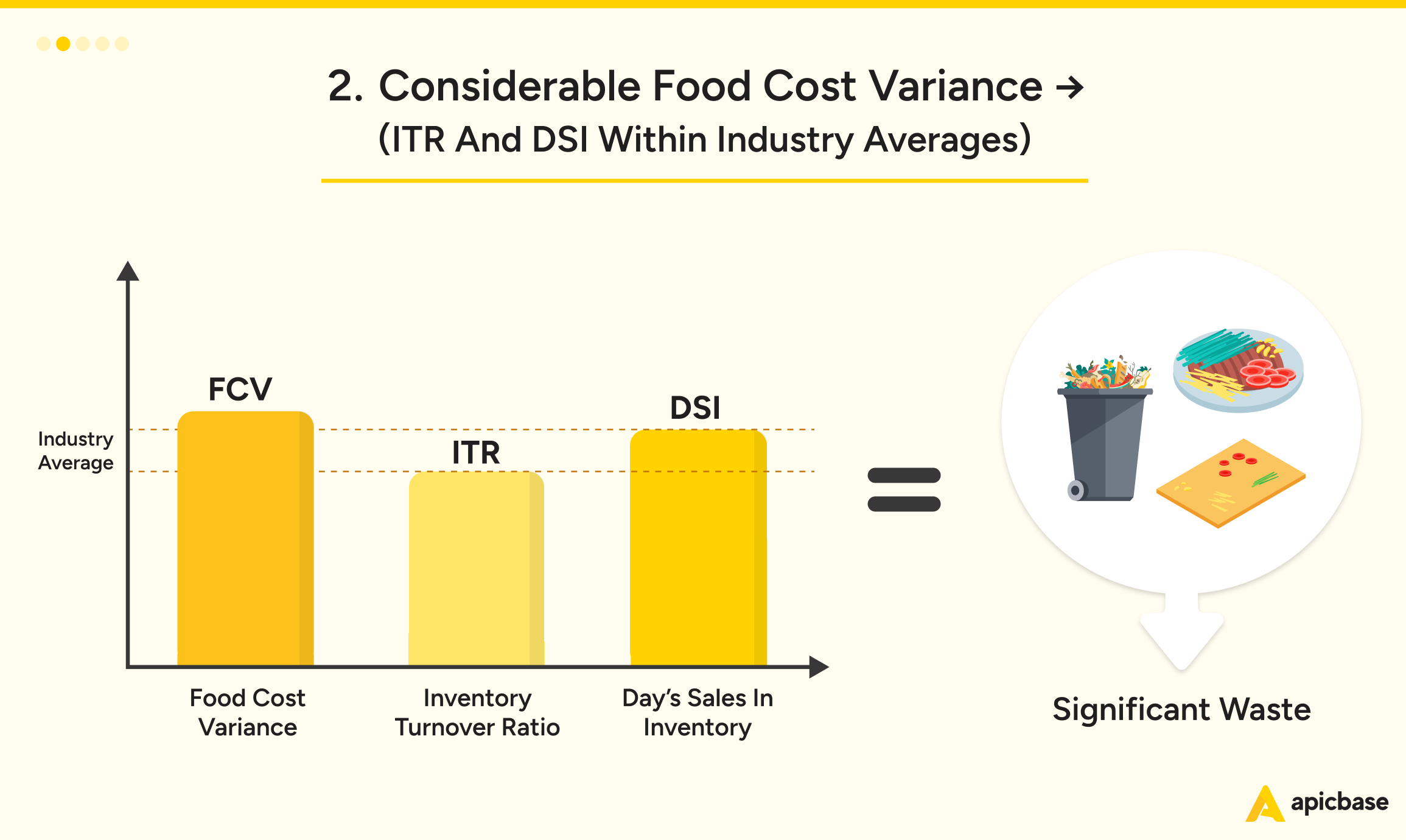
Significant food cost variance, despite inventory turnover (ITR) and days sales in inventory (DSI) being within industry averages, indicates waste somewhere in the pipeline. The usual suspects? Excessive trimming, over-plating, or theft.
To fix this:
- Run a Food Waste Audit: Track waste over a week to identify problem areas.
- Train Your Team: Reinforce proper food prep and plating techniques to minimise unnecessary waste.
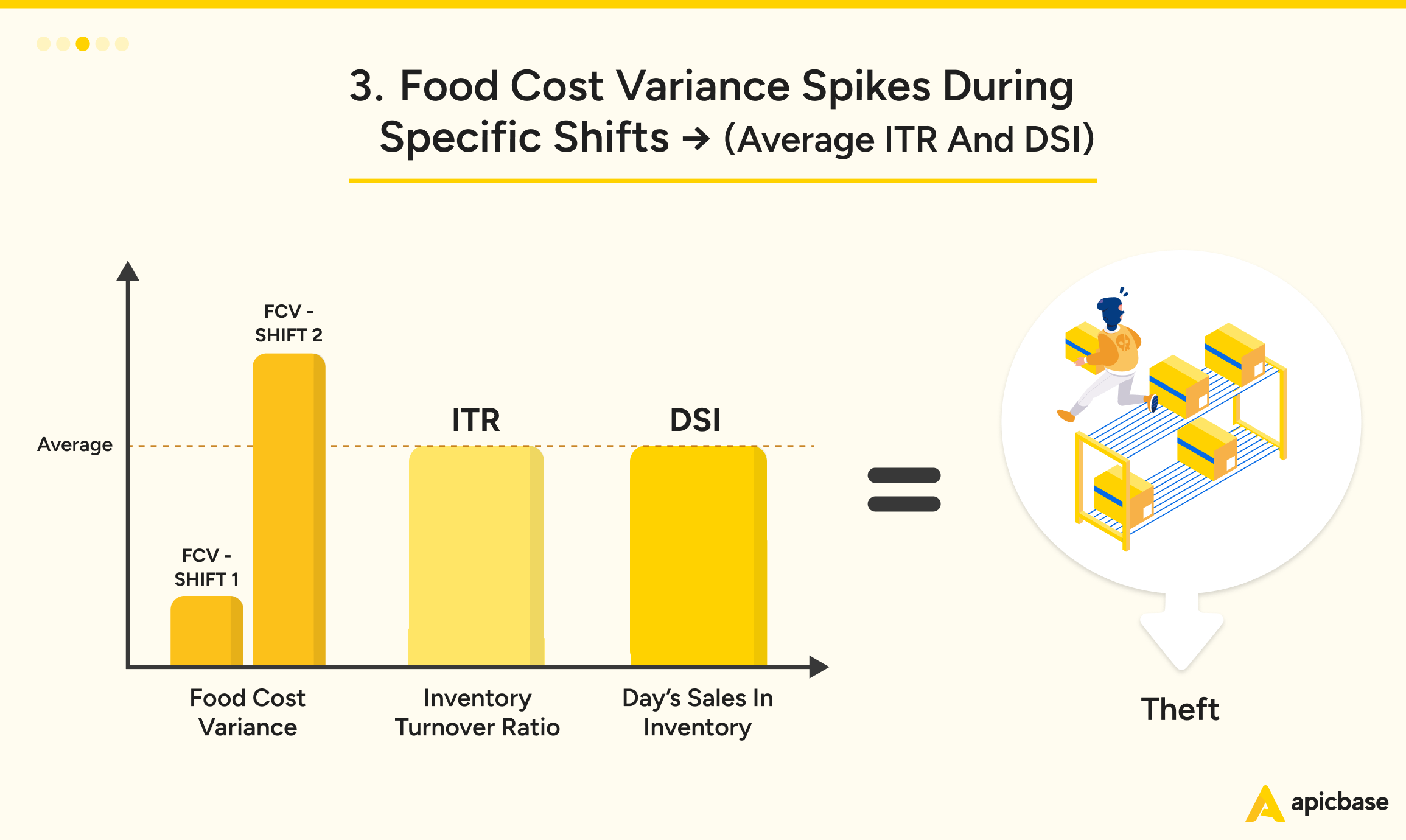
Spikes in food cost variance during specific shifts, despite average ITR and DSI, are a red flag. This often points to theft, a common issue in the restaurant industry, where employee theft is estimated to account for 4% of annual revenue loss.
To address this:
- Strengthen Inventory Controls: Implement stricter checks during and after shifts.
- Monitor High-Risk Areas: In extreme cases, consider installing surveillance in storerooms to deter theft.
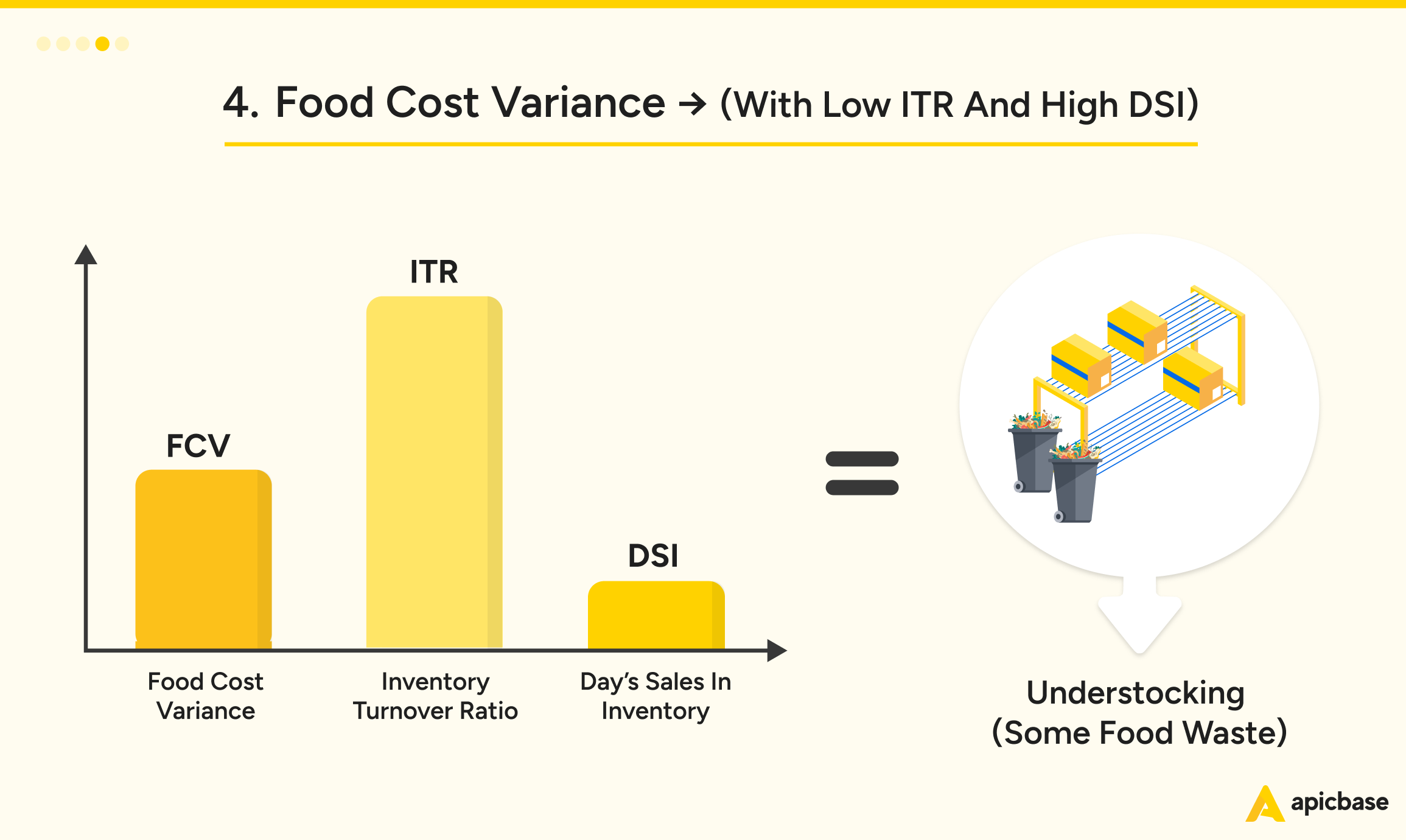
Moderate food cost variance, combined with high inventory turnover (ITR) and low days sales in inventory (DSI), likely means your team is understocking. This impacts customer satisfaction and your bottom line. While the variance isn’t severe, improper waste management still drives costs up.
To fix this:
- Audit Waste Control: Identify areas of unnecessary waste and take action to reduce it, driving food costs down.
- Use Sales Forecasts: Order the right stock quantities, including a safety buffer for high-demand items.
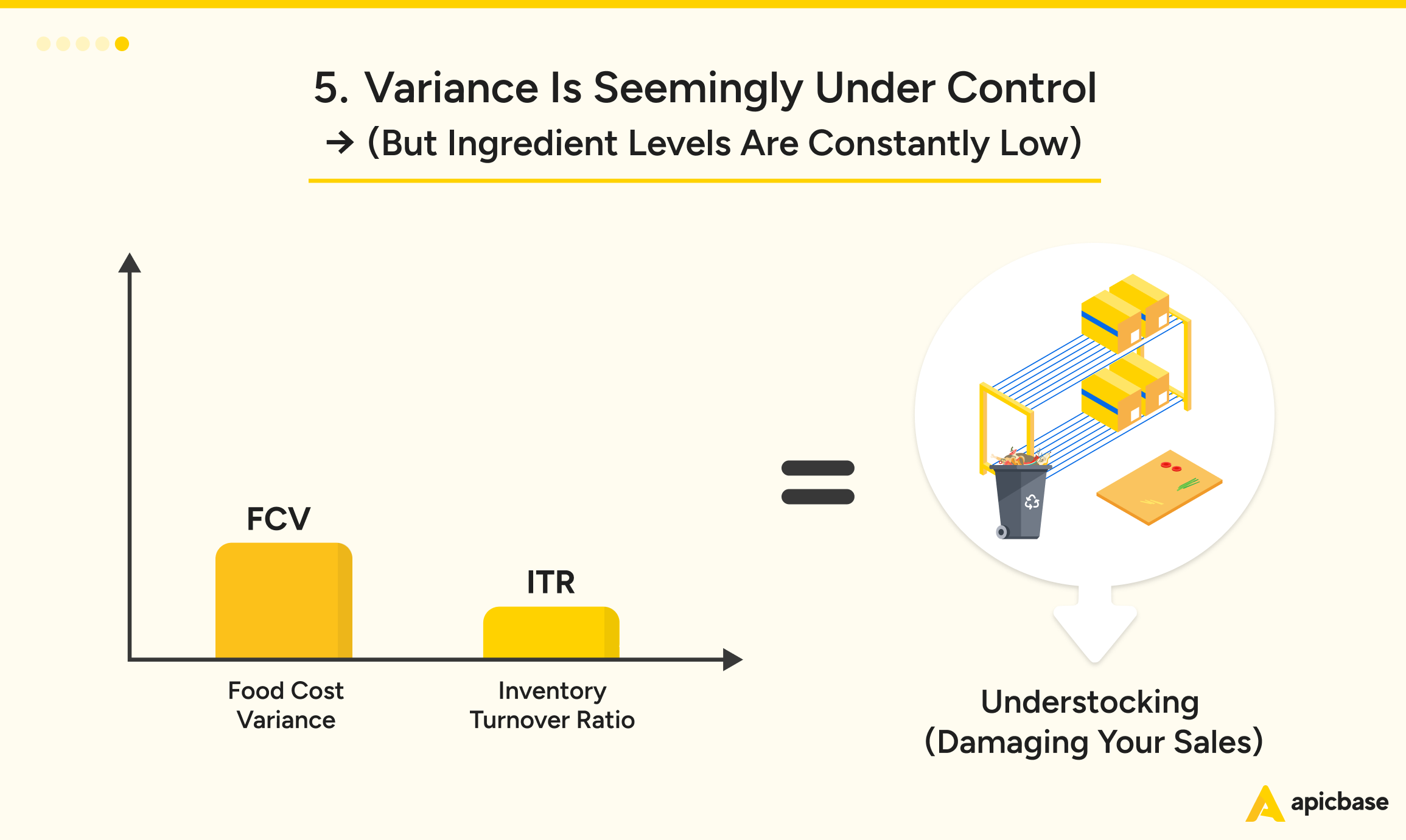
Variance appears under control, but ingredient levels are consistently low—this is a clear sign of understocking. While you’re managing food waste well, constantly running out of menu items hurts both sales and customer satisfaction.
To fix this:
- Add a Safety Margin: Include a buffer to prevent stockouts and reassess after a few weeks.
- Revise Par Levels: Adjust ingredient par levels to better meet demand.
These insights help you keep costs down and your customers happy.
If you take the time to monitor them —or better yet, use restaurant inventory software to get them instantly—you’ll make smarter purchasing decisions, fine-tune your menu for better profits, and cut down on food waste.
Use Case: Tackling Inventory Challenges During Rapid Expansion
“The gap between theoretical and actual food costs was widening, and we knew we had to fix it if we wanted to keep growing,” says Jay Greenslade, Operations Manager at The Avocado Show.
As the brand rapidly expanded across the Netherlands, UK, Spain, Belgium, and Germany, inventory management became a major headache. “Managing stock across multiple stores and franchised locations got chaotic fast,” Jay recalls. “We were either overstocking or understocking, which led to wasted food and hit our bottom line hard.”
To regain control, The Avocado Show turned to Apicbase. “It’s hands-down the most robust software for back-of-house management. The detailed cost tracking and its rock-solid Lightspeed POS connection made it an easy choice.”
The impact was immediate:
- No More Paperwork: “We’ve pretty much eliminated all paper and Excel files.”
- Clearer Data: “Now I can see what’s happening at every outlet—whether it’s overstocking, over-portioning, or something else.”
- Better Profitability: “We can catch discrepancies between theoretical and actual stock before they become big problems.”
- Franchise Consistency: “Apicbase makes sure all our locations follow the same inventory standards, which is so important for our model.”
“Apicbase has been a game-changer for our operations and expansion. It’s made inventory management consistent, efficient, and scalable.”
See Apicbase in Action
Keep inventory management simple, scalable, and reliable for all your restaurants.
Key Performance Indicators (KPI) for Inventory Management in Restaurants
As shown above, restaurant inventory management directly impacts your bottom line and operational efficiency, making it one of the most critical parts of your business.
Yet, without reliable data, it’s easy to lose control over what’s being purchased and used at each location.
The following metrics will help you stay on top of things.
1. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS tell you how much each restaurant spends on food and drink relative to sales. Keeping CoGS low is key to profitability.
Compare your CoGS regularly to your sales and budgets. Spot overspending or inefficiencies and fix them fast.
Formula: COGS = Starting Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory
Example:
- Starting inventory: €11.000
- Purchases: €7.000
- Ending inventory: €8.000
- COGS = €11.000 + €7.000 – €8.000 = €10.000
2. Food Cost Percentage (FCP)
The food cost percentage shows how much sales revenue is spent on food and drink. If this number is high, something needs adjusting—pricing, portions, or purchasing.
Check the FCP weekly to ensure you’re staying within your target range.
Formula: Food Cost Percentage = Food Cost / Total Sales × 100
Example:
- Food cost: €9.000
- Total sales: €25.000
- Food Cost Percentage = (€9.000 / €25.000) × 100 = 36%
3. Food Waste
Food waste is costly and impacts your margins. Knowing how much you are throwing away helps to address overproduction, spoilage and storage issues.
Track waste by weighing it daily and logging why it happened (e.g., spoilage, over-prep). Over time, these logs will reveal patterns. They tell a story. When does waste happen? Why? Are there specific teams or processes involved? Use this to set reduction actions and targets.
Tip: Assign a value to waste (e.g., €2,2/kg) to see its actual impact. This will help to keep people engaged.
Example:
- Food waste over two days: 53 kg
- Average cost of food: €2.2/kg
- Disposal cost: €0,20/kg
- Food Waste Cost = (53 × €2,2) + (50 × €0,20) = €126,60
Tip: Separate avoidable waste (e.g., leftovers) from unavoidable (e.g., trimmings). It will help you focus your efforts.
4. Inventory Turnover
Inventory Turnover shows how quickly you are using up stock. A high turnover means fresh ingredients, while a low turnover could signal overstocking or slow-moving items.
It’s best to track turnover rates by inventory category, as different types of stock have different needs:
- Highly Perishable Goods (e.g., fruits and vegetables) should have a fast turnover. Ideally, daily or 3-4 times a week.
- Dry Stock (e.g., rice, pasta) has a longer shelf life, so a slower turnover is expected. Aim to monitor usage trends and avoid overstocking.
- Drinks (e.g., soft drinks, bottled alcohol) often sell quickly but can also be stored longer. This allows you to buy in larger quantities without risking spoilage.
By categorising your inventory and tracking turnover rates for each, you can maintain freshness, reduce waste, and optimise storage space.
Formula: Inventory Turnover = COGS / Average Inventory Value
Example:
- COGS for the month: €66,000
- Average inventory: €33,000
- Inventory Turnover = €66,000 / €33,000 = 2 (or twice per month)
5. Prime Cost
Prime cost is the sum of food, beverage, and labour costs. It’s one of your largest expenses and a clear indicator of profitability.
Formula: Prime Cost = COGS + Labour Cost
Review prime cost monthly. Say you are a 30-unit restaurant chain with limited service. A prime cost above 60% might mean you need to look closer at staffing, purchasing practices, or menu pricing.
Example:
- COGS: €9,000
- Labour cost: €6,000
- Total sales: €25,000
- Prime Cost = €9,000 + €6,000 = €15,000
- Prime Cost Percentage = (€15,000 / €25,000) × 100 = 60%
6. Supplier Performance
Reliable suppliers save you and your team unnecessary headaches. Late deliveries or inconsistent quality disrupt operations, while last-minute purchases often cost more than planned bulk orders or negotiated supplier prices, cutting into profit margins.
Track how often orders are late, incomplete, or of poor quality. Share feedback with suppliers to improve service.
7. Stock Variance
Stock variance is the gap between what you should have (theoretical inventory) and what’s actually in stock. Variance highlights potential issues like theft, waste, or data errors.
- Theoretical/Recorded Inventory: Apicbase automatically calculates this based on purchases, usage, and sales data.
- Actual Inventory: This is the real, physical stock count in your kitchen or storage.
Stock variance actively reveals how well you are managing inventory.
For example, if your system says you should have 100 kg of chicken (theoretical inventory), but a physical count shows 90 kilograms (actual inventory), the variance is 10 kg.
Discrepancies might mean:
- Theft: When items go missing without being sold or recorded as used.
- Untracked Waste: Spoilage, over-prep, or over-portioning.
- Data Errors: Mistakes in entering purchases, waste logs or deliveries into the system.
Formula: Stock Variance = Recorded Inventory – Actual Inventory
Example:
- Recorded Inventory (Theoretical): €14,300
- Actual Inventory (Physical Count): €13,100
- Stock Variance: €4,300 – €13,100 = €1,200 variance
Apicbase tracks and displays variances in real time for each location.
8. Days Sales in Inventory (DSI)
DSI measures how many days it takes to sell your current inventory. A low DSI indicates efficient inventory turnover, while a high DSI might mean overstocking or slow-moving items. Lowering DSI improves liquidity and ensures you have cash available for other operational needs.
Track DSI to identify inefficiencies in stock management. Compare it against your category norms (e.g., perishables should have a lower DSI than dry goods) to optimise inventory levels.
Formula: DSI = (Average Inventory / COGS) × Days in Period
Example:
- Average inventory: €30,000
- COGS for the month: €60,000
- Days in period: 30
- DSI = (€30,000 / €60,000) × 30 = 15 days
How to Use Inventory KPIs in Daily Restaurant Operations
These KPIs are here to help, not overwhelm. The simpler you keep it, the better you will perform.
Follow this schedule to stay on top of stock and purchasing, keeping everything under control and running smoothly.
- Daily or Weekly Check-ins: Focus on Food Cost Percentage, Food Waste, and Inventory Turnover.
- Monthly Reviews: Look at COGS, Prime Cost, and Supplier Performance to spot trends and take action.
- Collaborative Approach: Discuss any roadblocks or insights during regular team meetings. Share what’s working and where you need support.
Restaurant Inventory Terminology
Effective inventory management hinges on how well your team follows protocols, and it all starts with understanding the basics. Every kitchen staff member should be familiar with these key terms
- Sitting Inventory: The total inventory currently available or in stock at the restaurant.
- Depletion: The amount of inventory used over a specific period, such as daily, weekly, or monthly.
- FIFO (First In, First Out): FIFO is an inventory rotation method that ensures older stock is used before newer stock, reducing the risk of spoilage.
- PAR Level (Periodic Automatic Replacement): Par Levels are the minimum and maximum stock you need for each item to avoid overstocking or running out
- Recipe Costing: Recipe costing is the process of calculating the total cost of ingredients used in a recipe to price menu items accurately.
- Waste and Spoilage: Inventory that is expired, damaged, or spoiled, representing a loss to the restaurant. Reducing food waste is critical for aligning operations with ESG principles while safeguarding profitability.
6 Reasons Multi-Unit Restaurants Choose Apicbase
- All-in-One Platform: Manage everything—ingredients, menus, suppliers, inventory, allergens, and performance metrics—in one centralised system.
- Consistency Across Locations: Uniform menu management, inventory tracking, and pricing ensure high quality and a seamless customer experience.
- Precise Inventory Tracking: Track ingredients, stock, and semi-finished goods with accuracy, eliminating waste and simplifying procurement.
- Powerful Analytics: Use detailed reports to reduce waste, forecast demand, and improve profitability across locations.
- Seamless Integrations: Connect with your POS, accounting software, and other tools for automated inventory.
- Scalable for Growth: Whether adding new locations or expanding menus, Apicbase grows with your business effortlessly.
Transform Your Restaurant Inventory Management with Apicbase
Inventory management has a direct impact on your restaurant’s profitability. Poor practices can quietly inflate your Cost of Goods Sold (CoGS), chipping away at your margins without notice.
This issue is even more pronounced in multi-site operations. Complex supply chains and numerous processes make it easy for losses to go unnoticed. These hidden leaks can push food costs over weeks or even months, and when spotted, tracing the cause is often difficult.
When restaurants prioritise inventory management, everything changes. Operations become smoother with faster, more accurate ordering. Food waste drops significantly. And most importantly, costs decrease consistently, week after week, delivering sustainable financial gains.
Ready to upgrade your inventory management system?

See Apicbase in Action
Keep inventory management simple, scalable, and reliable for all your restaurants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best inventory method for restaurants?
The FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method is the best choice for restaurants. It ensures older stock is used first, reducing waste and keeping food fresh. FIFO works with both periodic and perpetual inventory systems, making it ideal for managing perishables.
How much inventory should a restaurant carry?
The right amount depends on your sales, menu, and customer demand. Keep enough stock to avoid running out, but not so much that it leads to waste or high costs. Regularly adjust based on sales data and seasonal trends to find the balance.
Who is responsible for inventory in a restaurant?
Inventory is a team effort:
- Managers and chefs oversee ordering and stock tracking.
- Kitchen staff manage inventory at their stations.
- Shift managers monitor stock during shifts.
- Specialised staff may handle inventory in large or busy restaurants.
What should I look for in a restaurant inventory system?
Look for a system with these features:
- Integration with POS and other tools.
- Real-time tracking to monitor stock levels.
- Easy-to-use interface for all staff.
- Analytics and reporting to identify trends and control costs.
- Ordering tools that streamline procurement.
- Scalability to grow with your business.
- Mobile access for on-the-go inventory checks.